This post contains Solved Paper Financial Accounting I 2017 2nd Annual Punjab University, in which different topics of Financial Accountings are addressed such as Bills of Exchange, Final Accounts with Adjustments, Depreciation, Rectification of Errors, Non Trading Concern, Accounts from Incomplete Record, Partnership etc. All questions those are asked in the paper, are solved with great care and accuracy, if any error is found that will be purely mine. Other solutions and lectures posted on the subject such as Business Statistics and Mathematics are also available on the Website bcfeducation. Stay connected for the future solutions and lectures for all other topics of Accounting and Finance at all levels. Stay connected for the top notch solutions of different papers for Punjab University, University of Sargodha, FBISE, BISE LHR, BISE RWP, Delhi University, Mumbai University etc.
Solved by Iftikhar Ali, M.Sc Economics, MCOM Finance Lecturer Statistics, Finance and Accounting
Table of Contents
Solved Paper Financial Accounting I 2017 2nd Annual Punjab University
Q.1 For their mutual accommodation, Ahmad accepted a bill on 1st March, 2005, drawn on him by Aqeel for Rs. 12,000 at three months. The bill was got discounted at 10% p.a. and the proceeds were shared equally. ………. Aqeel in full settlement of his account. On 15th June, 2005, Aqeel became insolvent and his estate paid a dividend of 50 paisa in a rupee. Required: Give journal entries and Aqeel’s account in the books of Ahmad.
Q.1 For their mutual accommodation, Ahmad accepted a bill on 1st March, 2005, drawn on him by Aqeel for Rs. 12,000 at three months. The bill was got discounted at 10% p.a. and the proceeds were shared equally. On 1st April, 2005, Ahmad drew a bill for Rs. 18,000 on Aqeel at three months for the same purpose. Aqeel accepted the bill. Ahmad got the bill discounted at 10% p.a. and the proceeds were shared as 2/3 to Ahmad and 1/3 to Aqeel. Before the due date of the first bill Ahmad sent a cheque to Aqeel in full settlement of his account. On 15th June, 2005, Aqeel became insolvent and his estate paid a dividend of 50 paisa in a rupee.
Required: Give journal entries and Aqeel’s account in the books of Ahmad.
Solution:
Ahmad’s Journal
| Date | Detail | L.F | Dr. | Cr. |
| 2005 | ||||
| March, 1 | Aqeel Account | 12,000 | ||
| Bills Payable Account | 12,000 | |||
| (Acceptance given for three months to Aqeel) | ||||
| March, 1 | Bank Account | 5850 | ||
| Discount Account | 150 | |||
| Aqeel Account | 6000 | |||
| (Half the proceed of discounted bill is received from Aqeel) | ||||
| April, 1 | Bills Receivable Account | 18,000 | ||
| Aqeel Account | 18,000 | |||
| (Acceptance Received from Aqeel) | ||||
| April, 1 | Bank Account | 17,550 | ||
| Discount Account | 450 | |||
| Bills Receivable Account | 18,000 | |||
| (Bill Discounted from bank at 10%) | ||||
| April, 1 | Aqeel Account | 6,000 | ||
| Bank Account | 5850 | |||
| Discount Account | 150 | |||
| (1/3 of the proceed remitted to Aqeel) | ||||
| June,1 | Aqeel Account | 6000 | ||
| Bank Account | 6000 | |||
| (Amount sent to Aqeel by cheque for full settlement of his account) | ||||
| June, 4 | Bills Payable Account | 12,000 | ||
| Bank Account | 12,000 | |||
| (1st Bill met on maturity) | ||||
| June,15 | Aqeel Account | 18,000 | ||
| Bank Account | 18,000 | |||
| (2nd Bill dishonoured) | ||||
| June,15 | Cash Account | 9,000 | ||
| Bad Debts Account | 9,000 | |||
| Aqeel Account | 18,000 | |||
| (50% cash received from Aqeel and remaining is treated as bad debts) |
Aqeel’s Account
| Date | Detail | J.F | Dr. | Date | Detail | J.F | Cr. |
| 2005 | 2005 | ||||||
| March, 1 | Bills Payable Account | 12,000 | March, 1 | Bank Account | 5850 | ||
| April, 1 | Bank Account | 5850 | March, 1 | Discount Account | 150 | ||
| April, 1 | Discount Account | 150 | April, 1 | Bills Receivable Account | 18,000 | ||
| June,1 | Bank Account | 6000 | June,15 | Cash Account | 9,000 | ||
| June,1 | Bank Account | 18,000 | June,15 | Bad Debts Account | 9,000 | ||
| 42,000 | 42,000 |
Q.2 Prepare a Bank Reconciliation statement as on 31st December, 2015 from the following particulars.
Q.2 Prepare a Bank Reconciliation statement as on 31st December, 2015 from the following particulars.
i. Bank balance as per the Cash Book on 31st Dec. 2015, Rs. 77,000.
ii. Cheques for Rs. 17,000 deposited for collection but not credited by the bank prior to 31st December, 2015.
iii. Cheques amounting to Rs. 28,000 were issued on 28th December, out of which cheques for Rs. 25,000 were cashed up to 31st December, 2015.
iv. A wrong debit of Rs. 900 appeared in Pass Book.
v. Bank charges Rs. 520 appeared in the Pass Book but not in the Cash Book.
vi. Interest on investment collected by the bank not yet recorded in the Cash Book Rs. 3,500.
Solution
Bank Reconciliation Statement
As on 31st December 2005
| Balance as per the Cash Book Dr. | 77,000 |
| Less uncredited cheques | (17000) |
| Add unpresented cheques | 3000 |
| Less wrong debit by the bank in the pass book | (900) |
| Less Bank Charges appeared in the pass book | (520) |
| Add interest on investment collected by the bank | 3500 |
| Balance as per Pass Book Cr. | 65080 |
Q. 3 Rectify the following errors.
Q. 3 Rectify the following errors.
a. Rs. 840, a debit balance in Ahsan account are written off as bad debts, but only Rs. 480 were entered instead of Rs. 840, in addition to it Amir Account was credited instead of Ahsan A/c.
b. Rs. 2,000 paid for college fees of proprietor’s son were charged to the Trade Expenses account.
c. Bad debts recovered Rs. 500 from Amjad were credited to his account.
d. A receipt of Rs. 3,500 from Bilal & Co. was credited to his account as Rs. 5,300.
e. The total of the credit side of Ahmad A/c was overcast by Rs. 1000.
f. Sales Book was under-cast by Rs. 1,000.
g. Goods worth Rs. 1,000 were purchased from Nasir but were entered in the Sales Book. However, the account of Nasir was correctly credited.
h. The total of purchases returns book Rs. 2,000 was not posted to the ledger.
i. A credit balance of Rs. 7,550 of the Rent received Account was shown as Rs. 5,700.
j. Goods worth Rs. 6,200 sold to Usman, were correctly entered in the Sales Book, but posted to Usman A/c as Rs. 2,600.
Solution:
| S/No | Details | Dr. Rs. | Cr. Rs. |
| (a) | Amir Account | 480 | |
| Suspense Account | 360 | ||
| Ahsan Account | 840 | ||
| (being the Amir account wrongly credited and less credited ahsan’s account, now rectified) | |||
| (b) | Drawing Account | 2000 | |
| Trade Expenses Account | 2000 | ||
| (Being trade expenses account wrongly debited, now rectified) | |||
| (c) | Amjad’s Account | 500 | |
| Bad Debts Recovered Account | 500 | ||
| (Being Amjad’s account wrongly credited, now rectified) | |||
| (d) | Bilal & Co Account | 1800 | |
| Suspense Account | 1800 | ||
| (Being Bilal & Co account overstated, now rectified) | |||
| (e) | Ahmed’s Account | 1000 | |
| Suspense Account | 1000 | ||
| (Being Ahmed account credit side overstated, now rectified) | |||
| (f) | Suspense Account | 1000 | |
| Sales Account | 1000 | ||
| (Being Sales account understated, now rectified) | |||
| (g) | Purchases Account | 1000 | |
| Sales Account | 1000 | ||
| Nasir Account | 2000 | ||
| (Being the sales account wrongly credited, now rectified) | |||
| (h) | Suspense Account | ||
| Purchases Return Account | |||
| (Being purchases return account not posted, now rectified) | |||
| (i) | Suspense Account | 1850 | |
| Rent Received Account | 1850 | ||
| (Being the rent received understated, now rectified) | |||
| (j) | Usman Account | 3600 | |
| Suspense Account | 3600 | ||
| (Being the Usman account understated, now rectified) | |||
Q.4 The following is Receipts & Payments Account of Young men’s society for the year ending 31st December, 2005. You are required to prepare Income & Expenditure Account for the year ending 31st December, 2005.
Q.4 The following is Receipts & Payments Account of Young men’s society for the year ending 31st December, 2005. You are required to prepare Income & Expenditure Account for the year ending 31st December, 2005.
| Receipts | Rs. | Payments | Rs |
| Balance 1-1-2005 | 3485 | Books | 6150 |
| Entrance fees | 650 | Printing & Stationery | 465 |
| Donations | 6000 | Newspapers | 1110 |
| Subscription | 8565 | Sports Material Purchased | 5000 |
| Interest on Investments | 200 | Repairs | 650 |
| Sale of Furniture (Face Value 2000) | 1685 | Investments | 2000 |
| Sale of Old Papers | 465 | Furniture | 2000 |
| Receipts from recreation | 865 | Salaries | 1500 |
| Misc. Receipts | 125 | Balance 31-12-2005 | 3165 |
Capitalize Entrance Fee & Donations. Depreciation on Sports Material is 20%.
You are required to prepare Income & Expenditure Account for the year ending 31st December, 2005.
Solution:
Young men’s Society
Income & Expenditure A/C
For the year ended 31st December, 2005
| Expenditure | Amount | Income | Amount |
| Printing & Stationery | 465 | Subscriptions | 8565 |
| Newspapers | 1110 | Interest on investments | 200 |
| Repairs | 650 | Sale of old papers | 465 |
| Salaries | 1500 | Receipts from recreations | 865 |
| Loss on sale of furniture (2000 – 1685) | 315 | Miscellaneous receipts | 125 |
| Depreciation Sports Material 5000 (0.20) | 1000 | ||
| Surplus | 5180 | ||
| 10220 | 10220 |
Young men’s Society
Balance Sheet
At year ended 31st December, 2005
| Assets | Amount | Liabilities | Amount |
| Cash | 3165 | Capital: | |
| Investments | 2000 | Entrance fees 650 | |
| Sports Material Less Depreciation | Donations 6000 | ||
| (5000 – 1000) | 4000 | Cash opening 3485 | |
| Books | 6150 | 10135 | |
| Add Surplus 5180 | 15315 | ||
| 15315 | 15315 |
Q.5 From the following trial balance & adjustments, prepare trading & profit & loss account for the year ending 31st march, 2015 and a balance sheet as at 31-3-2015.
Q.5 From the following trial balance & adjustments, prepare trading & profit & loss account for the year ending 31st march, 2015 and a balance sheet as at 31-3-2015.
| Debit Balances | Rs. | Credit Balances | Rs. |
| Cash in hand | 3,000 | Sales | 843,000 |
| Cash at bank | 13,200 | Accounts Payable | 85,800 |
| Bills Receivable | 31,800 | Provision for Bad debts | 6,000 |
| Furniture | 60,000 | Bills Payable | 25,200 |
| Machinery | 168,000 | Capital | 360,000 |
| Drawings | 43,200 | ||
| Stock on 1-4-2014 | 123,000 | ||
| Purchases | 408,000 | ||
| Freight Inward | 9,000 | ||
| Accounts Receivable | 141,000 | ||
| Printing & Stationery | 10,200 | ||
| Salaries | 96,000 | ||
| Factory Rent | 24,000 | ||
| Insurance | 72,00 | ||
| Office Rent | 12,000 | ||
| Productive Wages | 129,000 | ||
| Manufacturing Expenses | 9,000 | ||
| Trade Expenses | 32,400 |
The following adjustments should be taken into account:
- Stationery unused on 31-3-2015 is Rs. 1800.
- Closing Stock valued at Rs. 170,000
- Write off Rs. 3,000 as bad debts and increase the provision for bad debts by 5% on accounts receivables.
- Depreciation machinery by 5% and furniture by 10%
- On 28th February, 2015 a fire broke out and destroyed stock of the value of Rs. 60,000 the stock was not covered by insurance.
Solution:
XXXX
Trading, Profit & Loss Account
For the year ended 31st Mar 2015
| Particulars | Rs | Particulars | Rs. |
| Opening Stock | 123,000 | Closing Stock | 170,000 |
| Purchases | 408,000 | Sales | 843,000 |
| Freight Inward | 9,000 | Loss of Stock by Fire | 60,000 |
| Productive Wages | 129,000 | ||
| Factory Rent | 24,000 | ||
| Manufacturing Expenses | 9,000 | ||
| Gross Profit c/d | 371,000 | ||
| 10,73,000 | 10,73,000 | ||
| Salaries | 96,000 | Gross Profit b/d | 371,000 |
| Trade Expenses | 32,400 | ||
| Depreciation on Furniture | |||
| 60,000 x 0.10 | 6000 | ||
| Depreciation on Machinery | |||
| 168,000 x 0.05 | 8400 | ||
| Insurance | 72,00 | ||
| Office Rent | 12,000 | ||
| Printing & Stationery 10,200 | |||
| Less Stock Unused (18,00) | 8400 | ||
| Bad Debts 0 | |||
| Add Write Off 3,000 | |||
| Add New Provision: | |||
| (141,000 – 3000) x 0.05 6900 | |||
| Less Old Provision (6,000) | 3900 | ||
| Loss of Stock by Fire | 60,000 | ||
| Net Profit Transferred to Balance Sheet | 136,700 | ||
| 371,000 | 371,000 | ||
XXXX
Balance Sheet
As on year ended 31st Mar 2015
| Liabilities | Rs | Assets | Rs. |
| Capital & Owner’s Equity: | Fixed Assets: | ||
| Capital 360,000 | Furniture Less Depreciation: | ||
| Less Drawings (43,200) | (60,000 – 6000) | 54,000 | |
| Add Net Profit 136,700 | 453,500 | Machinery Less Depreciation: | |
| (168,000 – 8400) | 159,600 | ||
| Current Assets: | |||
| Debentures & Long Term Liabilities: | Cash in hand | 3,000 | |
| Nil | 0 | Cash at bank | 13,200 |
| Stationery Unused Closing Stock | 1800 | ||
| Closing Stock | 170,000 | ||
| Current Liabilities: | Bills Receivable | 31,800 | |
| Accounts Payable | 85,800 | Accounts Receivable 141,000 | |
| Bills Payable | 25,200 | Less Write Off (3000) | |
| Less New Provision (6900) | 131,100 | ||
| Reserves: | 0 | ||
| 564,500 | 564,500 |
Q.6 Zulfiqar and Ahmad are partners in a firm sharing profits and losses as Zulfiqar ¾ and Ahmad¼ on 1st January, 2005;their position was as given below……..Riaz is now to join the partnership. He agrees to pay the partners Rs. 20,000 by way of goodwill and introduces 3/5 of the combined capital of the two existing partners after depreciating plant and stock at 20% and 10% respectively and raising a reserve of 10% against Sundry Debtors. The new partner is to be allowed 1/4th share of the profits of the firm. You are required to record the above transactions in the books of the firm and give the resultant balance sheet of the new firm.
Q.6 Zulfiqar and Ahmad are partners in a firm sharing profits and losses as Zulfiqar ¾ and Ahmad¼ on 1st January, 2005;their position was as given below:
| Assets | Rs. | Liabilities | Rs. |
| Plant | 40,000 | Capital Accounts: | |
| Stock | 10,000 | Mr. Zulfiqar 50,000 | |
| Debtors | 30,000 | Mr. Ahmad 30,000 | 80,000 |
| Cash at Bank | 20,000 | Sundry Creditors | 20,000 |
Riaz is now to join the partnership. He agrees to pay the partners Rs. 20,000 by way of goodwill and introduces 3/5 of the combined capital of the two existing partners after depreciating plant and stock at 20% and 10% respectively and raising a reserve of 10% against Sundry Debtors. The new partner is to be allowed 1/4th share of the profits of the firm.
You are required to record the above transactions in the books of the firm and give the resultant balance sheet of the new firm.
Solution:
Journal
| Date | Particulars | L.F | Dr. | Cr. |
| Revaluation A/C | 12000 | |||
| Plant & Machinery A/C | 8000 | |||
| Reserve for Bad Debts A/C | 3000 | |||
| Stock A/C | 1000 | |||
| (Value of the asset is reduced and reserve for bad debt raised W:1 & W:2 & W:3) | ||||
| Zulfiquar’s Capital A/C | 9000 | |||
| Ahmad’s Capital A/C | 3000 | |||
| Revaluation A/C | 12000 | |||
| (Loss of Revaluation distributed between partners in ratio 3:1 W:4) | ||||
| Cash A/C | 72,800 | |||
| Riaz’s Capital A/C | 52,800 | |||
| Goodwill A/C | 20,000 | |||
| (Riaz introduces capital and goodwill W:5) | ||||
| Goodwill A/C | 20,000 | |||
| Zulfiquar’s Capital A/C | 15000 | |||
| Ahmad’s Capital A/C | 5000 | |||
| (Goodwill distributed between old partners in ratio 3:1 W:6) |
New Balance Sheet of the New Firm
| Assets | Rs. | Liabilities | Rs. |
| Plant & Machinery less Depreciation | Capital Accounts: | ||
| (40,000 – 8000) | 32,000 | Zulfiqar | |
| Stock (10,000 – 1000) | 9000 | (50,000 – 9000 + 15000) | 56000 |
| Sundry Debtors 30,000 | Ahmad | ||
| Less Write Off (0) | (30,000 – 3000 + 5000) | 32000 | |
| Less New Provision (3000) | 27,000 | Riaz | 52800 |
| Cash at Bank (20,000 + 72,800) | 92800 | Sundry Creditors | 20,000 |
| 160,800 | 160,800 |
New Profit Sharing Ratio of Zulfiqar and Ahmad & Riaz
Data:
Zulfiqar’s Old Ratio=3/4
Ahmad’s Old Ratio=1/4
Riaz’s Ratio=1/4
Remaining Ratio=1-1/4=3/4
Zulfiqar‘s New Ratio=(3/4)(3/4)=9/16
Ahmad‘s New Ratio=(1/4)(3/4)=3/16
New Ratio of Zulfiqar:Ahmad:Riaz=9/16:3/16:1/4
New Ratio of Zulfiqar:Ahmad:Riaz=9/16:3/16:4/16
New Ratio of Zulfiqar:Ahmad:Riaz=9:3:4
W:1 Calculation of Depreciation of Plant
40,000 x 0.20 = 8000
W: 2 Calculation of Reserve of Bad Debts Raised
30,000 x 0.10 = 3000
W:3 Calculation of Depreciation of Stock
10,000 x 0.10 = 1000
W:4 Calculation of Revaluation Loss of Old Partners
Zulfiqar’s Share=12000×3/4=9000
Ahmad’s Share=12000×1/4=3000
W:5 Calculation of Riaz’s Capital
Riaz’s Capital=88,000×3/5=52800
W:6 Calculation of Goodwill distributed to old partners
Zulfiqar’s Share=20000×3/4=15000
Ahmad’s Share=20000×1/4=5000
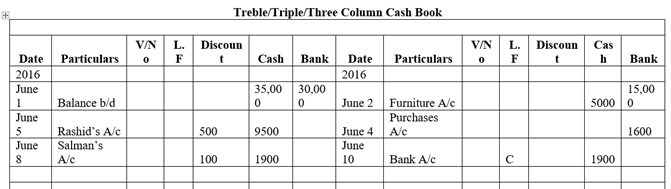
Q.7 Define cash book. Explain different types of cash book. Also provide the specimen of three column cash book.
Answer: A cash book is a financial journal that records all cash receipts and cash payments, including bank deposits and withdrawals. It is a crucial part of the accounting records for any business, serving both as a ledger and a journal. The cash book is regularly reconciled with the bank statements to ensure accuracy and completeness of the records.
Types of Cash Books
There are several types of cash books, each serving different purposes:
Single Column Cash Book:
Purpose: Records only cash transactions.
Structure: Has one column each for cash receipts and cash payments.
Usage: Suitable for small businesses with simple cash transactions and no bank transactions.
Double Column Cash Book:
Purpose: Records both cash and bank transactions.
Structure: Has two columns for receipts (cash and bank) and two columns for payments (cash and bank).
Usage: Suitable for businesses that handle both cash and bank transactions regularly.
Triple Column Cash Book:
Purpose: Records cash, bank transactions, and discounts.
Structure: Has three columns for receipts and payments: cash, bank, and discount.
Usage: Useful for businesses that frequently offer or receive discounts along with regular cash and bank transactions.
Petty Cash Book:
Purpose: Records small, routine, and repetitive expenditures.
Structure: Often includes various columns for different types of petty expenses (e.g., postage, stationery, travel expenses).
Usage: Managed by a petty cashier and used to keep track of minor business expenses.
Specimen of Three Column Cash Book
Q.8 A firm purchased a second-hand truck for Rs. 50,000 on 1st January, 2002 and spent Rs. 20,000 on its overhauling. Depreciation is written off at the rate of 10% p.a. On 30th June, 2005 the truck was sold for Rs. 30,000 being unsuitable. Prepare the Truck Account from 2002 to 2005 assuming that Accounts are closed on 31st December every year under the following methods. 1. Straight line method. 2. Written down value method.
Solution:
1. Truck Account under Straight Line Method
Truck Account
| Date | Detail | Rs. | Date | Detail | Rs. |
| 1-1-2002 | Cash A/C | 50,000 | 31-12-2002 | Depreciation A/C | 7,000 |
| 1-1-2002 | Cash A/C | 20,000 | 70,000 (0.10)=7000 | ||
| 31-12-2002 | Balance c/d | 63,000 | |||
| 70,000 | 70,000 | ||||
| 1-1-2003 | Balance b/d | 63,000 | 31-12-2003 | Depreciation A/C | 7,000 |
| 70,000 (0.10)=7000 | |||||
| 31-12-2003 | Balance c/d | 56,000 | |||
| 63,000 | 63,000 | ||||
| 1-1-2004 | Balance b/d | 56,000 | 31-12-2004 | Depreciation A/C | 7,000 |
| 70,000 (0.10)=7000 | |||||
| 31-12-2004 | Balance c/d | 49,000 | |||
| 56.000 | 56.000 | ||||
| 1-1-2005 | Balance b/d | 49,000 | 30-6-2005 | Depreciation A/C | 3500 |
| 70000 (0.10)(6/12) | |||||
| 30-6-2005 | Cash A/C | 30,000 | |||
| 30-6-2005 | P&L A/C (Loss) W:1 | 15,500 | |||
| 51,030 | 51,030 |
W:1 Calculation of Profit or Loss
| Cost | 70,000 |
| Less Depreciation for 2002 | (7,000) |
| Less Depreciation for 2003 | (7,000) |
| Less Depreciation for 2004 | (7,000) |
| Less Depreciation for 2005 | (3,500) |
| Book Value at the time of Sale | 45,500 |
| Selling Price Realized | (30,000) |
| Loss | 15,500 |
2. Truck Account under Written Down Value Method
Truck Account
| Date | Detail | Rs. | Date | Detail | Rs. |
| 1-1-2002 | Cash A/C | 50,000 | 31-12-2002 | Depreciation A/C | 7,000 |
| 1-1-2002 | Cash A/C | 20,000 | 70,000 (0.10)=7000 | ||
| 31-12-2002 | Balance c/d | 63,000 | |||
| 70,000 | 70,000 | ||||
| 1-1-2003 | Balance b/d | 63,000 | 31-12-2003 | Depreciation A/C | 6,300 |
| 63,000 (0.10)=6300 | |||||
| 31-12-2003 | Balance c/d | 56,700 | |||
| 63,000 | 63,000 | ||||
| 1-1-2004 | Balance b/d | 56,700 | 31-12-2004 | Depreciation A/C | 5,670 |
| 56,700 (0.10)=5670 | |||||
| 31-12-2004 | Balance c/d | 51,030 | |||
| 56.700 | 56.700 | ||||
| 1-1-2005 | Balance b/d | 51,030 | 30-6-2005 | Depreciation A/C | 2551.5 |
| 51030 (0.10)(6/12) | |||||
| 30-6-2005 | Cash A/C | 30,000 | |||
| 30-6-2005 | P&L A/C (Loss) W:2 | 18478.5 | |||
| 51,030 | 51,030 |
W:2 Calculation of Profit or Loss
| Cost | 70,000 |
| Less Depreciation for 2002 | (7,000) |
| Less Depreciation for 2003 | (6,300) |
| Less Depreciation for 2004 | (5,670) |
| Less Depreciation for 2005 | (2551.5) |
| Book Value at the time of Sale | 48478.5 |
| Selling Price Realized | (30,000) |
| Loss | 18,478.5 |
You might be interested in the following
Solved Paper Financial Accounting I 2023 Punjab University
Solved Paper Financial Accounting I 2022 Punjab University
Solved Paper Financial Accounting I 2023 Punjab University
Business Statistics and Mathematics Solved Paper 2012, Punjab University, BCOM, ADC I
Business Statistics & Mathematics, Solved Paper 2011, Punjab University, BCOM,ADCI
Business Statistics & Mathematics, Solved Paper 2010, Punjab University, BCOM, ADCI
Partnership Profit Distribution ICOM/DBA II
Partnership Admission of a Partner ICOM/DBA II