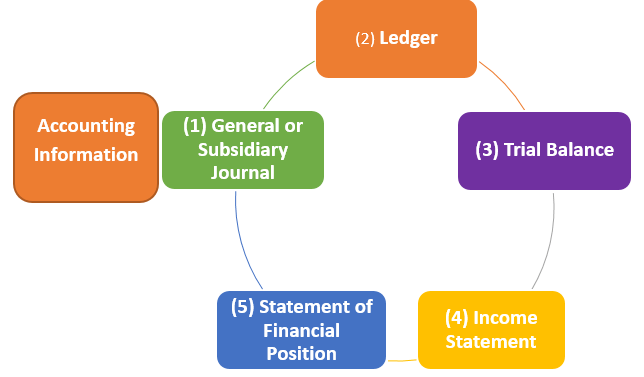
Cambridge IGCSE/O Level Accounting Topic 2: Sources and recording of data
Written by Iftikhar Ali M.Com/M.Sc Economics
Double Entry Book-keeping
Double Entry Book-keeping is a method to record business transaction in which two aspects of transaction are recorded. These two aspects are receiving and giving. These two aspects are also called debit and credit & in all types of journals both sides must be equal. In each transaction at-least two accounts are used. In our course we shall directly record transactions into ledgers. Here rules for debit and credit are important to understand. These rules are given below in table 2.1 below:
| Account | Debit (Dr.) | Credit (Cr.) |
| Assets | + Increase | Decrease |
| Expenses | + Increase | Decrease |
| Liabilities | Decrease | + Increase |
| Capital | Decrease | + Increase |
| Revenue/Income | Decrease | + Increase |
Each transaction must be recorded twice as debit and credit in the ledger. Format of ledger account is given below:
| Account Name | |||||||
| Dr. | Cr. | ||||||
| Date | Details | Folio | $ | Date | Details | Folio | $ |

Example 1:
20-7
January 1 Ajay began business. He opened a business bank account and invested $80 000 as capital.
2 Fixtures and equipment costing $30 000 were bought and paid for by cheque.
Enter these transactions in Ajay’s ledger.
| Date | Detail | Folio | Dr. $ | Cr. $ |
| January 1 | Bank A/C | 80,000 | ||
| Capital A/C | 80,000 | |||
| (Ajay introduced capital through depositing into bank) | ||||
| January 2 | Fixture & Equipment A/C | 30,000 | ||
| Bank A/C | 30,000 | |||
| (Fixture & equipment purchased & paid through bank) |
| Bank Account | |||||||
| Dr. | Cr. | ||||||
| Date | Details | Folio | $ | Date | Details | Folio | $ |
| 20-7 | 20-7 | ||||||
| January 1 | Capital | 80,000 | January 2 | Fixture & Equipment | 30,000 | ||
| Capital Account | |||||||
| Dr. | Cr. | ||||||
| Date | Details | Folio | $ | Date | Details | Folio | $ |
| 20-7 | |||||||
| January 1 | Bank | 80,000 | |||||
| Furniture & Equipment Account | |||||||
| Dr. | Cr. | ||||||
| Date | Details | Folio | $ | Date | Details | Folio | $ |
| 20-7 | |||||||
| January 2 | Bank | 30,000 | |||||
Double entry records for assets and liabilities
Favorable balance of assets is debit or you can say that whenever you receive asset, must be debited & favorable balance of liabilities is credit means whenever obligation becomes due on you, you must credit that economic or financial obligation. In reverse case, credit the assets and debit the liabilities if asset is going out and liabilities are paid respectively.
Example 2:
20–7
January 1 Ajay began business. He opened a business bank account and invested $80 000 as capital
2 Fixtures and equipment costing $30 000 were bought and paid for by cheque.
3 A short-term loan of $10 000 was received from AB Loans.
5 A motor vehicle costing $9 000 was bought and paid for by cheque.
6 A long-term loan of $5 000 was received from Ajay’s sister Mallika.
Enter these transactions in Ajay’s ledger.
Solution:
You are not required to prepare Journal instead directly record into ledger accounts but here, we are going to make journal entry first to understand posting into ledger accounts.
| Date | Detail | Folio | Dr. $ | Cr. $ |
| 20-7 | ||||
| January 1 | Bank A/C | 80,000 | ||
| Capital A/C | 80,000 | |||
| (Ajay introduced capital through depositing into bank) | ||||
| January 2 | Fixture & Equipment A/C | 30,000 | ||
| Bank A/C | 30,000 | |||
| (Fixture & equipment purchased & paid through bank) | ||||
| January 3 | Bank A/C | 10,000 | ||
| AB Loans A/C | 10,000 | |||
| (Short term loan is taken from AB Loans) | ||||
| January 5 | Motor Vehicle A/C | 9,000 | ||
| Bank A/C | 9,000 | |||
| (Motor Vehicle purchased, paid through bank) | ||||
| January 6 | Bank A/C | 5,000 | ||
| Malika Loan A/C | 5,000 | |||
| (Long term loan is acquired from Malika) |
| Bank Account | |||||||
| Dr. | Cr. | ||||||
| Date | Details | Folio | $ | Date | Details | Folio | $ |
| 20-7 | 20-7 | ||||||
| January 1 | Capital | 80,000 | January 2 | Fixture & Equipment | 30,000 | ||
| January 3 | AB Loans | 10,000 | January 5 | Motor Vehicle | 9,000 | ||
| January 6 | Malika Loan | 5,000 | |||||
| Capital Account | |||||||
| Dr. | Cr. | ||||||
| Date | Details | Folio | $ | Date | Details | Folio | $ |
| 20-7 | |||||||
| January 1 | Bank | 80,000 | |||||
| Furniture & Equipment Account | |||||||
| Dr. | Cr. | ||||||
| Date | Details | Folio | $ | Date | Details | Folio | $ |
| 20-7 | |||||||
| January 2 | Bank | 30,000 | |||||
| AB Loans Account | |||||||
| Dr. | Cr. | ||||||
| Date | Details | Folio | $ | Date | Details | Folio | $ |
| 20-7 | |||||||
| January 3 | Bank | 10,000 | |||||
| Motor Vehicle Account | |||||||
| Dr. | Cr. | ||||||
| Date | Details | Folio | $ | Date | Details | Folio | $ |
| 20-7 | |||||||
| January 5 | Bank | 9,000 | |||||
| Malika Loan Account | |||||||
| Dr. | Cr. | ||||||
| Date | Details | Folio | $ | Date | Details | Folio | $ |
| 20-7 | |||||||
| January 6 | Bank | 5,000 | |||||
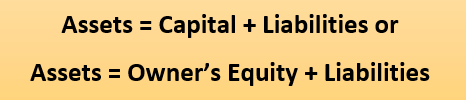
Double entry records for expenses & income
Favorable balance for expense is debit and for income is credit which means when expenses occur, account title of expense must be debited and when income is received, account title of income must be credited in Journal. For ledger accounts, the rule is same as discussed above.
Example 3:
20–7
January 1 Ajay began business with a capital of $80 000 in the business bank account
1 He paid rent of premises, $400, by cheque
2 Fixtures and equipment costing $30 000 were bought and paid for by cheque
3 He paid insurance, $250, by cheque
3 A short-term loan of $10 000 was received from AB Loans
5 A motor vehicle costing $9 000 was bought and paid for by cheque
5 He paid motor expenses, $50, by cheque
6 A long-term loan of $5 000 was received from Ajay’s sister Mallika
7 Part of the premises were rented out to another business and a cheque for $95 was received.
Post them into ledgers and also balance the accounts.
Solution:
You are not required to prepare Journal instead directly record into ledger accounts but here, we are going to make journal entry first to understand posting into ledger accounts.
| Date | Detail | Folio | Dr. $ | Cr. $ |
| 20-7 | ||||
| January 1 | Bank A/C | 80,000 | ||
| Capital A/C | 80,000 | |||
| (Ajay introduced capital through depositing into bank) | ||||
| January 1 | Rent Payable A/C | 400 | ||
| Bank A/C | 400 | |||
| (Rent paid by cheque) | ||||
| January 2 | Fixture & Equipment A/C | 30,000 | ||
| Bank A/C | 30,000 | |||
| (Fixture & equipment purchased & paid through bank) | ||||
| January 3 | Insurance A/C | 250 | ||
| Bank A/C | 250 | |||
| (Insurance paid by cheque) | ||||
| January 3 | Bank A/C | 10,000 | ||
| AB Loans A/C | 10,000 | |||
| (Short term loan is taken from AB Loans) | ||||
| January 5 | Motor Vehicle A/C | 9,000 | ||
| Bank A/C | 9,000 | |||
| (Motor Vehicle purchased, paid through bank) | ||||
| January 5 | Motor Expense A/C | 50 | ||
| Bank A/C | 50 | |||
| (Motor expense paid by cheque) | ||||
| January 6 | Bank A/C | 5,000 | ||
| Malika Loan A/C | 5,000 | |||
| (Long term loan is acquired from Malika) | ||||
| January 7 | Bank A/C | 95 | ||
| Rent Receivable A/C | 95 | |||
| (Rent received for building rented out by cheque) |
| Bank Account | |||||||
| Dr. | Cr. | ||||||
| Date | Details | Folio | $ | Date | Details | Folio | $ |
| 20-7 | 20-7 | ||||||
| January 1 | Capital | 80,000 | January 1 | Rent Payable | 400 | ||
| January 3 | AB Loans | 10,000 | January 2 | Fixture & Equipment | 30,000 | ||
| January 6 | Malika Loan | 5,000 | January 3 | Insurance | 250 | ||
| January 7 | Rent Receivable | 95 | January 5 | Motor Vehicle | 9,000 | ||
| January 5 | Motor Expense | 50 | |||||
| January 7 | Balance | c/d | 55395 | ||||
| 95095 | 95095 | ||||||
| 20-7 | |||||||
| January 8 | Balance | b/d | 55395 | ||||
| Capital Account | |||||||
| Dr. | Cr. | ||||||
| Date | Details | Folio | $ | Date | Details | Folio | $ |
| 20-7 | |||||||
| January 7 | Balance | c/d | 80,000 | January 1 | Bank | 80,000 | |
| 80000 | 80000 | ||||||
| 20-7 | |||||||
| January 8 | Balance | b/d | 80,000 | ||||
| Furniture & Equipment Account | |||||||
| Dr. | Cr. | ||||||
| Date | Details | Folio | $ | Date | Details | Folio | $ |
| 20-7 | 20-7 | ||||||
| January 2 | Bank | 30,000 | January 7 | Balance | c/d | 30,000 | |
| 30000 | 30000 | ||||||
| 20-7 | |||||||
| January 8 | Balance | b/d | 30,000 | ||||
| AB Loans Account | |||||||
| Dr. | Cr. | ||||||
| Date | Details | Folio | $ | Date | Details | Folio | $ |
| 20-7 | 20-7 | ||||||
| January 7 | Balance | c/d | 10,000 | January 3 | Bank | 10,000 | |
| 10000 | 10000 | ||||||
| 20-7 | |||||||
| January 8 | Balance | b/d | 10,000 | ||||
| Motor Vehicle Account | |||||||
| Dr. | Cr. | ||||||
| Date | Details | Folio | $ | Date | Details | Folio | $ |
| 20-7 | 20-7 | ||||||
| January 5 | Bank | 9,000 | January 7 | Balance | c/d | 9,000 | |
| 9000 | 9000 | ||||||
| 20-7 | |||||||
| January 8 | Balance | b/d | 9,000 | ||||
| Malika Loan Account | |||||||
| Dr. | Cr. | ||||||
| Date | Details | Folio | $ | Date | Details | Folio | $ |
| 20-7 | 20-7 | ||||||
| January 7 | Balance | c/d | 5,000 | January 6 | Bank | 5,000 | |
| 5000 | 5000 | ||||||
| 20-7 | |||||||
| January 8 | Balance | b/d | 5,000 | ||||
| Rent Payable Account | |||||||
| Dr. | Cr. | ||||||
| Date | Details | Folio | $ | Date | Details | Folio | $ |
| 20-7 | 20-7 | ||||||
| January 1 | Bank | 400 | January 7 | Balance | c/d | 400 | |
| 400 | 400 | ||||||
| 20-7 | |||||||
| January 8 | Balance | b/d | 400 | ||||
| Insurance Account | |||||||
| Dr. | Cr. | ||||||
| Date | Details | Folio | $ | Date | Details | Folio | $ |
| 20-7 | 20-7 | ||||||
| January 3 | Bank | 250 | January 7 | Balance | c/d | 250 | |
| 250 | 250 | ||||||
| 20-7 | |||||||
| January 8 | Balance | b/d | 250 | ||||
| Motor Expense Account | |||||||
| Dr. | Cr. | ||||||
| Date | Details | Folio | $ | Date | Details | Folio | $ |
| 20-7 | 20-7 | ||||||
| January 5 | Bank | 50 | January 7 | Balance | c/d | 50 | |
| 50 | 50 | ||||||
| 20-7 | |||||||
| January 8 | Balance | b/d | 50 | ||||
| Rent receivable Account | |||||||
| Dr. | Cr. | ||||||
| Date | Details | Folio | $ | Date | Details | Folio | $ |
| 20-7 | 20-7 | ||||||
| January 7 | Balance | c/d | 95 | January 7 | Bank | 95 | |
| 95 | 95 | ||||||
| 20-7 | |||||||
| January 8 | Balance | b/d | 95 | ||||
Double entry records for Drawings, Sales, Purchase, Returns & Carriage
Drawings is the value which is taken out by the owner for his/her personal use. It may be in monetary terms or physical term such as goods or non-current asset. Invested amount or physical asset by the owner is called capital which has credit favorable balance whereas drawing is reduction in capital so it will be considered debit. When drawing occurs, drawing account is debited whereas cash or bank account is credited, if cash is taken out from the business for personal use. In case of non-current asset, that non-current asset account is credited and when goods are taken out as drawing, purchases account is credited.
Purchases
When goods are purchased for resale purposes, it must be recorded at cost price. It may be on cash basis in which purchases account is debited and cash or bank account is credited if payment is made by cash or through cheque respectively. In case of credit purchases, creditor or supplier account is credited.
Purchases return or Return outward
Sometimes purchased goods are returned to the supplier may be due to faulty goods or unwanted goods. If transaction was made on cash or cheque based, cash or bank account is debited and purchases return or return outward account is credited. If purchase transaction was based on credit, supplier or creditor account is debited and purchases return or return outward account is credited.
Sales
When purchased goods (those are purchased for resale purpose) are sold to the customer it must be recorded on sales price. If goods are sold on cash or cheque basis, cash or bank account is debited and sales account is credited. When it is sold on credit, debtor or customer account is debited and sales account is credited.
Sales return or Return Inward
Sometimes sold goods are returned by customer due to faulty goods or unwanted goods, it is called sales return or return inward. If sold goods are sold on cash or cheque based, Sales return or return inward account is debited and Cash or bank account is credited whereas if transaction was credit based, customer account or debtor account is credited and sales return or return inward account is debited.
Carriage
Carriage is the cost of transporting goods, it is an expense and expenses always has debit favorable balance. Carriage has two types, one is called carriage inward and other is called carriage outward.
Carriage inward
Carriage inward is carriage paid or payable to transporting goods to the business location. It is considered as direct expense. Carriage inward account is debited and cash or bank account is credited, if it is paid and supplier account is credited if it is payable.
Carriage outward
Carriage paid for transportation of goods to the customer. It is selling or indirect expense. Carriage outward account is debited and cash or bank account is credited, if it is paid and supplier account is credited if it is payable.
Example 4:
20–7
January 1 Ali began business with a capital of $100 000 in the business bank account
1 He paid rent of premises, $400, by cheque
2 Fixtures and equipment costing $30 000 were bought and paid for by cheque
3 Ali purchased goods, $820, on credit from Samit
4 Ali purchased goods $500 and paid by cheque.
5 Carriage inward $50 paid by cheque.
5 Ali sold goods, $245, on credit to Kamal Traders
6 Kamal Traders returned damaged goods, $55, to Ali
6 Kamal Traders paid their account by cheque
7 Ali returned faulty goods, $44, to Samit
7 Carriage outward $75 paid through cheque.
7 Ali gave Samit a cheque for $700 on account.
7 Ali withdrawn $ 200 through cheque for his personal use, goods $100 and furniture $500.
Enter these transactions in Ajay’s ledger.
Solution:
You are not required to prepare Journal instead directly record into ledger accounts but here, we are going to make journal entry first to understand posting into ledger accounts.
| Date | Detail | Folio | Dr. $ | Cr. $ |
| 20-7 | ||||
| January 1 | Bank A/C | 100,000 | ||
| Capital A/C | 100,000 | |||
| (Ajay introduced capital through depositing into bank) | ||||
| January 1 | Rent Payable A/C | 400 | ||
| Bank A/C | 400 | |||
| (Rent paid by cheque) | ||||
| January 2 | Fixture & Equipment A/C | 30,000 | ||
| Bank A/C | 30,000 | |||
| (Fixture & equipment purchased & paid through bank) | ||||
| January 3 | Purchases A/C | 820 | ||
| Samit A/C | 820 | |||
| (Goods are purchased from Samit on credit) | ||||
| January 4 | Purchases A/C | 500 | ||
| Bank A/C | 500 | |||
| (Goods are purchased and paid by cheque) | ||||
| January 5 | Carriage Inward A/C | 500 | ||
| Bank A/C | 500 | |||
| (Carriage Inward paid) | ||||
| January 5 | Kamal Traders A/C | 245 | ||
| Sales A/C | 245 | |||
| (Goods are sold on credit to Kamal Traders) | ||||
| January 6 | Sales return A/C | 55 | ||
| Kamal Traders A/C | 55 | |||
| (Damaged goods are returned by Kamal Traders) | ||||
| January 6 | Bank A/C | 190 | ||
| Kamal Traders A/C | 190 | |||
| (Balance amount is received from Kamal Traders) | ||||
| January 7 | Samit A/C | 44 | ||
| Purchases Return A/C | 44 | |||
| (Faulty goods are returned to Samit) | ||||
| January 7 | Carriage outward A/C | 75 | ||
| Bank A/C | 75 | |||
| (Carriage outward is paid by cheque) | ||||
| January 7 | Samit A/C | 700 | ||
| Bank A/C | 700 | |||
| (Amount paid to Samit) | ||||
| January 7 | Drawings A/C | 800 | ||
| Bank A/C | 200 | |||
| Purchases A/C | 100 | |||
| Furniture A/C | 500 | |||
| (Ali withdrawn amount, goods and furniture for his personal use) |
| Bank Account | |||||||
| Dr. | Cr. | ||||||
| Date | Details | Folio | $ | Date | Details | Folio | $ |
| 20-7 | 20-7 | ||||||
| January 1 | Capital | 100,000 | January 1 | Rent Payable | 400 | ||
| January 6 | Kamal Traders | 190 | January 2 | Fixture & Equipment | 30,000 | ||
| January 4 | Purchases | 500 | |||||
| January 5 | Carriage Inward | 500 | |||||
| January 7 | Carriage outward | 75 | |||||
| January 7 | Samit | 700 | |||||
| January 7 | Drawings | 200 | |||||
| January 7 | Balance | c/d | 67815 | ||||
| 100190 | 100190 | ||||||
| 20-7 | |||||||
| January 8 | Balance | b/d | 67815 | ||||
| Capital Account | |||||||
| Dr. | Cr. | ||||||
| Date | Details | Folio | $ | Date | Details | Folio | $ |
| 20-7 | |||||||
| January 7 | Balance | c/d | 100,000 | January 1 | Bank | 100,000 | |
| 100000 | 100000 | ||||||
| 20-7 | |||||||
| January 8 | Balance | b/d | 100,000 | ||||
| Rent Payable Account | |||||||
| Dr. | Cr. | ||||||
| Date | Details | Folio | $ | Date | Details | Folio | $ |
| 20-7 | 20-7 | ||||||
| January 1 | Bank | 400 | January 7 | Balance | c/d | 400 | |
| 400 | 400 | ||||||
| 20-7 | |||||||
| January 8 | Balance | b/d | 400 | ||||
| Furniture & Equipment Account | |||||||
| Dr. | Cr. | ||||||
| Date | Details | Folio | $ | Date | Details | Folio | $ |
| 20-7 | 20-7 | ||||||
| January 2 | Bank | 30,000 | January 7 | Drawings | 500 | ||
| January 7 | Balance | c/d | 29500 | ||||
| 30000 | 30000 | ||||||
| 20-7 | |||||||
| January 8 | Balance | b/d | 29500 | ||||
| Purchases Account | |||||||
| Dr. | Cr. | ||||||
| Date | Details | Folio | $ | Date | Details | Folio | $ |
| 20-7 | 20-7 | ||||||
| January 3 | Samit | 820 | January 7 | Drawings | 100 | ||
| January 4 | Bank | 500 | January 7 | Balance | c/d | 1220 | |
| 1320 | 1320 | ||||||
| 20-7 | |||||||
| January 8 | Balance | b/d | 1220 | ||||
| Purchases Return Account | |||||||
| Dr. | Cr. | ||||||
| Date | Details | Folio | $ | Date | Details | Folio | $ |
| 20-7 | 20-7 | ||||||
| January 7 | Balance | c/d | 44 | January 7 | Samit | 44 | |
| 44 | 44 | ||||||
| 20-7 | Balance | b/d | 44 | ||||
| Samit’s Account | |||||||
| Dr. | Cr. | ||||||
| Date | Details | Folio | $ | Date | Details | Folio | $ |
| 20-7 | 20-7 | ||||||
| January 7 | Purchases return | 44 | January 3 | Purchases | 820 | ||
| January 7 | Bank | 700 | |||||
| January 7 | Balance | c/d | 76 | ||||
| 820 | 820 | ||||||
| 20-7 | |||||||
| January 8 | Balance | b/d | 76 | ||||
| Carriage Inward Account | |||||||
| Dr. | Cr. | ||||||
| Date | Details | Folio | $ | Date | Details | Folio | $ |
| 20-7 | 20-7 | ||||||
| January 5 | Bank | 500 | January 7 | Balance | c/d | 500 | |
| 500 | 500 | ||||||
| 20-7 | |||||||
| January 8 | Balance | b/d | 500 | ||||
| Kamal Traders Account | |||||||
| Dr. | Cr. | ||||||
| Date | Details | Folio | $ | Date | Details | Folio | $ |
| 20-7 | 20-7 | ||||||
| January 5 | Sales | 245 | January 6 | Sales Return | 55 | ||
| January 6 | Bank | 190 | |||||
| 245 | 245 | ||||||
| Sales Account | |||||||
| Dr. | Cr. | ||||||
| Date | Details | Folio | $ | Date | Details | Folio | $ |
| 20-7 | 20-7 | ||||||
| January 7 | Balance | c/d | 245 | January 5 | Kamal Traders | 245 | |
| 245 | 245 | ||||||
| 20-7 | |||||||
| January 8 | Balance | b/d | 245 | ||||
| Sales Return Account | |||||||
| Dr. | Cr. | ||||||
| Date | Details | Folio | $ | Date | Details | Folio | $ |
| 20-7 | 20-7 | ||||||
| January 6 | Kamal Traders | 55 | January 7 | Balance | c/d | 55 | |
| 55 | 55 | ||||||
| 20-7 | |||||||
| January 8 | Balance | b/d | 55 | ||||
| Carriage Outward Account | |||||||
| Dr. | Cr. | ||||||
| Date | Details | Folio | $ | Date | Details | Folio | $ |
| 20-7 | 20-7 | ||||||
| January 7 | Bank | 75 | January 7 | Balance | c/d | 75 | |
| 75 | 75 | ||||||
| 20-7 | |||||||
| January 8 | Balance | b/d | 75 | ||||
| Drawings Account | |||||||
| Dr. | Cr. | ||||||
| Date | Details | Folio | $ | Date | Details | Folio | $ |
| 20-7 | 20-7 | ||||||
| January 7 | Bank | 200 | January 7 | Balance | c/d | 800 | |
| Purchases | 100 | ||||||
| Furniture | 500 | ||||||
| 800 | 800 | ||||||
| 20-7 | |||||||
| January 8 | Balance | b/d | 800 | ||||
Note: To visit Topic 1 please click the link below: