Evolving different thoughts of Economics. “Economic thought has evolved through centuries, shaping the way we understand wealth, markets, and human behavior. The journey begins with Adam Smith’s classical economics, where the ‘invisible hand’ and the pursuit of self-interest lay the foundation for market dynamics. Later, Alfred Marshall’s neo-classical economics refined these ideas, introducing concepts like marginal utility and supply-demand equilibrium. Finally, Lionel Robbins’ modern approach redefined economics as the science of scarcity and choice, focusing on the allocation of limited resources to meet endless wants. Together, these perspectives offer a comprehensive view of economic theory’s evolution.”
Written by Iftikhar Ali
Important Topic for all boards and university students such as FBISE, BISERWP, BISE LHR, MU, SU, PU, UOD etc.
For learning of Economics, Statistics, Finance, Investment, Accounting and Business Subjects visit bcfeducation
Table of Contents
Evolving different thoughts of Economics
There are multiple definitions of economics but here we can distribute these definitions into three groups:
- Classical School of though. (Economics is a science of wealth)
- Neo-Classical School of thought. (Economics is a science of material welfare)
- Modern. (Economics is a science of scarcity and choice)
Classical School of thought (Economics is a Science of Wealth)
Adam Smith’s Definition of Economics
Adam Smith is considered as Father of Economics. He provided foundational definition of Economics in his Book “Wealth of Nations” published in 1776. He belongs to Classical School of thoughts. They believe that Economics is a science of wealth. According to Adam Smith’s point of view, Economics can be defined as:
“Economics is a science which discusses the production of wealth, consumption of wealth, distribution of wealth and exchange of wealth”
Production of Wealth
Simply means how wealth is produced. There are four factors of production, land, labor, capital and organization. When these four factors combine with each other, they produce goods and services. These goods and services produce wealth.
Consumption of Wealth
Consumption of wealth simply means that how we spend part of wealth on our necessities of life.
Distribution of Wealth
According to Adam Smith, wealth is produced by combining four factors of production, land, labor, capital and organization and there are rewards for each of them, rent for land, wages for labor, interest for capital and profit for organization.
Exchange of Wealth
Exchange of wealth means that how wealth passes from one person to other and one country to other country by means of international trade.
Other Classical Economists about Economics
F.A Walker
“Economics is a science which deals with wealth”
Chapman
“Economics studies all human activities which deal with wealth”
J.B. Say
“Economics discusses the activities which deal with wealth”
J.S Mill
“Economics is the science of production of wealth and distribution of wealth”
Objection Criticism on Classical thought about Economics
- Moralists Ruskin and Carlyle named it as a memmon (evil, demon) science that promotes worldly desires.
- Contemporary moralists considered it as science of bread and butter.
- Objective of study of wealth is not mentioned.
- Purpose of human activities as production, consumption, distribution and exchange of wealth is not cleared.
- It makes the people greedy, selfish and unsympathetic
Response to Criticism
After analyzing above criticism, point is clear that critics took narrow meaning of wealth, they just considered wealth as money and they considered that all the people who are performing these activities are evil. This is not fair because struggle to fulfill basic needs of life is not unfair. Struggle to earn food and butter is not selfishness. Wealth itself is not a bad thing but its use may be bad or good. For example, if somebody is creating wealth in gambling or in any other unlawful activity, is wrong but its positive use to earn fair life needs is not only good but also direly needed. If there is no wealth, how can we build hospitals, universities, schools and perform other meaningful activities. It is a basic trigger of movement all around the world.
Neo-Classical thought of Economics (Economics is a Science of Material Welfare)
Alfred Marshal’s Definition of Economics
“A study of mankind in the ordinary business of life. It examines the part of individual and social action which is most closely connected with the attainment and use of material requisites of well-being”
This definition is often regarded as the best as it covers all of the actions that humans take to earn and spend their income & it provides link between wealth and welfare.A.C Pigou, Cannon, Clark and Pareto all the economists gave the definitions of economics in the same line so we can say that these are all the supporters of Alfred Marshal’s point of view.
ATTRIBUTES OF THE DEFINITION
- Ordinary Business of Life
According to Alfred Marshal, Economics is a social science which studies human behavior in a society so all those persons who do not take any part in the economic activities such as mad or mentally ill persons are excluded.
- Analysis of Economic Activities
People perform multiple activities in a society and there are multiple subjects for each type of activity. For example, subject of sociology covers the social activities, Political science for political activities similarly economics is for economic activities.
- Welfare of the Society
According to Alfred Marshal, basic objective is not to achieve and consume wealth. Wealth is only mean to achieve welfare of the society so food, shelter, clothing etc. should be produced on priority basis not the luxury goods.
- Economics is a Social Science
Economics is a social science rather than individual centric. In economics, we examine individuals who live in societies where they both impact and are influenced by others.
- Study of Physical Activities
This concept states that economics exclusively looks at tangible activities, as those performed by masons, carpenters, and other craftsmen. The work of educators, physicians, engineers, and other service providers has been disregarded.
- Economic Aspect of Life
According to this definition, economics simply looks at the financial side of things, ignoring social, religious, political, and other facets of existence. The economic side concerns a man’s means of earning and allocating his money.
- Attainment and use of Material Requisite
At this point Alfred Marshal follows the Adam Smith point of that economic activities are related to production of wealth and consumption of wealth in order to accomplish the objective of material welfare.
CRITICISM
Professor Lionel Robbins harshly objected to Marshals’ explanation of economics. He identified the following definitional flaws:
1.Narrow Concept of the Subject
According to Marshall’s definition, only those activities that create material items are addressed in economics, and the service sector of the firm has been completely ignored. Marshall focused primarily on material welfare as a result of the material goods. This turned out to be one of the definition’s most contentious aspects.
2. Narrow Meaning of Wealth
Marshal’s explanation is categorical. Economic phenomena have been divided into material and non-material categories. However, the notion of economics simply acknowledges the satisfying of material requirements.
3. Ambiguity in Definition
Marshal did not clear the difference between ordinary business of life and extra ordinary business of life.
4. Welfare cannot be measured
As a mental state, welfare cannot be assessed statistically and is hence unquantifiable. It is impossible to quantify the precise quantity of wellbeing or to pinpoint the precise amount of satisfaction that may be obtained from purchases, performances, or activities. All that can be done is assume. For example, it would be very hard to determine, quantify, or even estimate the welfare benefit that two friends would make by buying the same good.
5. Economics is not Purely a Social Science
According to Marshals, economics is a social science. He asserts that while the topic is concerned with all individuals as members of society, a guy living in a forest is outside its purview. However, Robbins countered that economics is the study of all people, regardless of their social status. It is therefore preferable to refer to economics as “human science.”
6. Objection on Welfare
Marshal only focused on activities which promotes human material welfare but all other aspects are excluded those are not welfare oriented such as drugs, cigarettes, alcoholic drinks are excluded from the definition but keep in mind that they also give satisfaction to the persons who use them.
Modern thought of Economics (Economics is a Scarcity & choice)
After Alfred Marshal, Lionel Robins gave his point of view about economics in the following way:
“Economics is a science which studies human behavior as a relationship between multiple ends and scarce means which have alternative uses.”
Robins highlighted four facts of human life given below:
Multiple Ends
Multiple ends mean that human wants or desires are unlimited and most of them remains unsatisfied.
Scarce Resources
Most of wants or desires remains unsatisfied because there are limited resources to fulfill all wants.
All Wants are not equal in importance
Third point of view of Robins definition that all wants are not equal in importance and human prefers most important and needed wants first.
Alternative Uses
All wants are not equal in importance so human has to choose most important first to satisfy. For example, a human has limited amount to spend either on food or dress so he has to choose food first.
Merits or Attributes of Robins Definition
Comprehensive
Definition given by Robins is comprehensive and clear based on facts of daily human life. Nobody can deny scarce resources and unlimited wants. Similarly, inequality in importance of wants and alternative uses adopted by humans are unquestionable.
Scientific
Definition given by Robins is scientific because concept of scarce resources is measurable whereas concept of welfare given by Alfred Marshal is unmeasurable.
Universal
Definition given by Robins is universal in context. It can be applied on each and every part of the world. In the context of wants and scarce resources, all the humans are equal in response to these issues.
Neutral
Definition given by Robins is purely in positive context and he remains neutral in which he just discussed realities of daily human life and did not use the normative style to tackle these issues.
Scope
Scope in his definition of economics is wider than other economists because his definition covers material and non-material issues both. As Alfred Marshal just covered the welfare side.
Drawbacks & Criticism
Narrow Focus on Scarcity and Choice
Critics argue that Robbins’ definition is too narrow, as it focuses exclusively on scarcity and choice, overlooking other important aspects of economics like production, distribution, and consumption.
Neglect of Welfare and Human Well-being
Robin’s definition ignores the welfare aspect of economics so classical and neo classical economists criticized that welfare aspect of life must be taken into account for the betterment of the society.
Ethical Neutrality
Robin’s definition has ethical neutrality so critics think that only material aspect consideration is not enough because decisions affects the human life.
Economics is a Science and Art
Robins discussed economics in purely scientific view under positive aspect of science in which only issue can be discussed whereas it is also an art to solve the economic problem and we can say that normative aspect is missing.
Economics cannot be Neutral
In real life, economics cannot be neutral, we have to solve the problems because people expect to solve the problem.
Conclusion
Despite all criticism on Robin’s definition, it is most popular definition of economics because nobody can deny the fact that humans have unlimited wants or desires and to fulfill these demands they have scarce resources but all wants are not equal in importance so they have to choose most important first. We can say that Economics is the study of choices made by people for the best ultimate use of scarce resources.
You might be interested in the following:
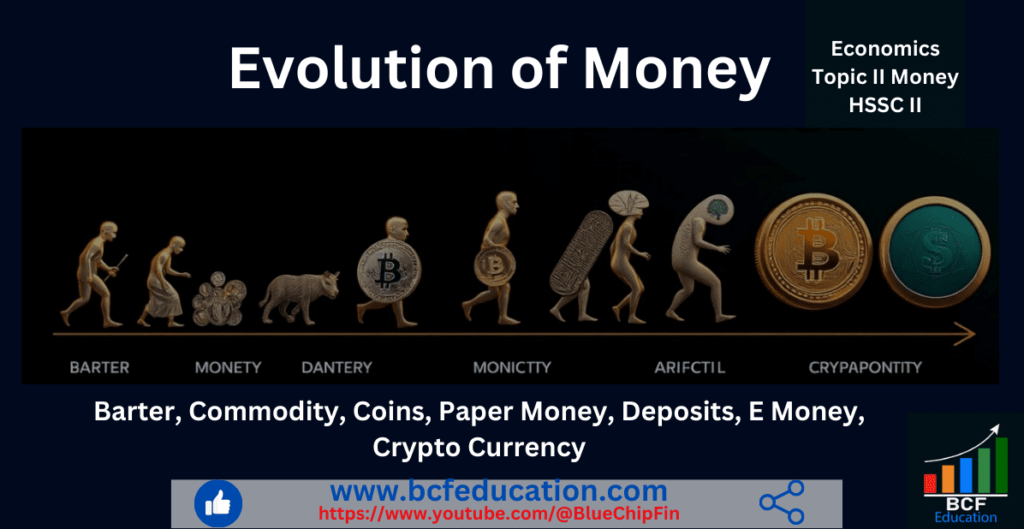
Barter System and its Difficulties
Evolving different thoughts of Economics
2.1 Theory of Consumer Behaviour
2.2 Total Utility, Marginal Utility, Point of Satiety & Types of Utilities