In this post Change and Shift in Demand, Extension and Contraction in Demand, Rise and Fall in Demand, we explore key concepts in demand analysis. These principles help us understand how various factors influence consumer demand and how shifts in price and income levels impact market behavior. Essential for economics, business, and finance students, this post provides a clear breakdown of these microeconomic concepts to build a strong foundation in demand theory. This topic is equally important for the students of economics across all the major Boards and Universities such as FBISE, BISERWP, BISELHR, MU, DU, PU, NCERT, CBSE & others & across all the business & finance disciplines.
Table of Contents
Change and Shift in Demand, Extension and Contraction in Demand, Rise and Fall in Demand
Change and Shift in Demand
Introduction
Quantity demand inversely related with price but there are other factors also, those who change the quantity demand such as income, taste, price of substitutes, prices of complementary goods etc. Change in the demand has two types, one is called extension and contraction of the demand and other one is called rise and fall in demand.
Extension and Contraction in Demand
When quantity demand changes due to change in price, is called extension and contraction of the quantity demand and this change does not shift the demand curve up and down but remains on the same line. For understanding, observe the table and diagram given below:
| Price of Apple (Rs.) | Quantity Demand of Apple (kg) |
| 300 | 2 |
| 200 | 4 |
| 100 | 6 |

Explanation
Above table shows that when price of apple is Rs. 300, the demand for apple is 2 kg which is shown in the figure above at Q1 point whereas when it price drops to Rs. 200, its demand rises to 4 kg and this point is shown in the figure at Q2. When price of apple falls to Rs. 100, its quantity demand rises to 6 kg which is shown in above figure at point Q3. So when quantity demand increases, it moves on same line downward which is called extension and when quantity demand decreases due to price, it moves upward on the same line which is called contraction of the quantity demand.
Rise and Fall in Demand
When quantity demand changes not due to price but other factors such as income, weather, taste etc., the change is called rise and fall in demand. Here rise means increase in demand and fall means decrease in demand. In rise and fall in demand, change does not move on the same line but shifts the line above and below the demand line. Here we are going to explain these two behaviors with the help of table and diagram below:
Rise in Demand
Table Rise in Demand
| Price of Eggs (Rs/Dozen) | Original Demand Summer (Dozen) | Increased Demand Winter (Dozen) |
| 300 | 20 | 60 |
| 280 | 40 | 80 |
| 260 | 60 | 100 |
| 240 | 80 | 120 |
| 220 | 100 | 140 |
| 200 | 120 | 160 |
Figure Rise in Demand

Explanation
Here original demand of eggs in summer is given above and as well as quantity demand of eggs in winter is given and it is clearly shown that due to change in weather, the demand for eggs is increased suddenly that causes the shift of demand line to above the original demand line which is called rise or increase in demand.

Fall in Demand
Table Fall in Demand
| Price of Eggs (Rs/Dozen) | Original Demand Winter (Dozen) | Decreased Demand Summer (Dozen) |
| 300 | 60 | 20 |
| 280 | 80 | 40 |
| 260 | 100 | 60 |
| 240 | 120 | 80 |
| 220 | 140 | 100 |
| 200 | 160 | 120 |
Figure Fall in Demand
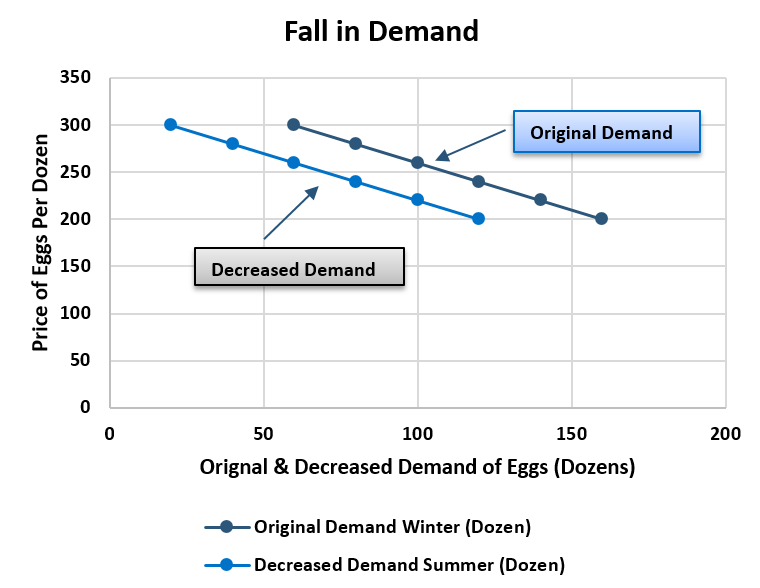
Explanation
Here original demand of eggs in winter is given above and as well as quantity demand of eggs in summer is given and it is clearly shown that due to change in weather, the demand for eggs is decreased suddenly that causes the shift of demand line to below the original demand line which is called fall or decrease in demand.
Related Articles
Evolving different thoughts of Economics
2.1 Theory of Consumer Behaviour
2.2 Total Utility, Marginal Utility, Point of Satiety & Types of Utilities
2.3 The Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility DMU
2.4 The Law of Equal Marginal Utility EMU
3.1 Demand, Individual Demand, Aggregate Demand, Law of Demand
3.2 Change and Shift in Demand, Extension and Contraction in Demand, Rise and Fall in Demand