In this post, I’ll explore the barter system and its difficulties, an early method of trade where goods and services were exchanged directly without money. We’ll also delve into the challenges it presented, making it an important topic in both economics and business.
Written by Iftikhar Ali
Important Topic for all boards and university students such as FBISE, BISERWP, BISE LHR, MU, SU, PU, UOD etc.
For learning of Economics, Statistics, Finance, Investment, Accounting and Business Subjects visit bcfeducation
Table of Contents
Barter System and its Difficulties
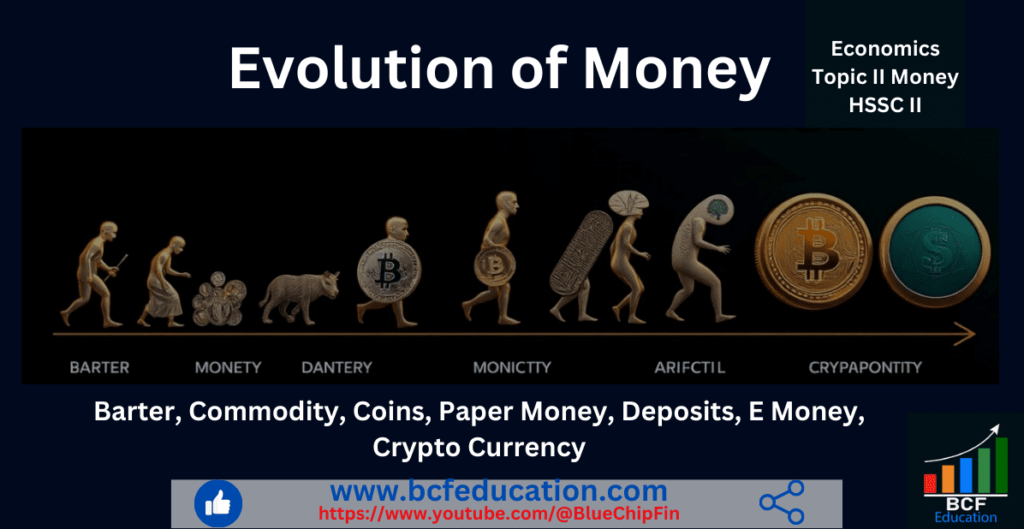
Money
For everyone, young or old, male or female, educated or not, rich or poor, intelligent or foolish, money has always been a fascinating term. On the one hand, various people have varied demands and preferences when it comes to material items. For example, a youngster may be interested in toys and chocolates; a student may desire books; a woman may be eager to purchase more makeup; a hungry person may want food; and a homeless person may dream of owning a home.
On the other hand, the desire to obtain money is typical because money is a medium of exchange goods and services. Each of them believes that possessing money will satisfy their material needs. Earliest use of money was occurred in Mesopotamia (Iraq) around 2500 BC
Definitions of Money
According to Walker “Money is what money does”.
According to Morgan “Money is anything that is widely used in payments of debts”.
According to Samuelson “Money is the modern medium of exchange and the standard unit in
which prices and debts are expressed.”
Barter System
If we study the human history, we find that human used to live in caves and hunt for the food. Human used the skin of animals and leaves to cover their bodies. They had limited desires and they did not rely on others for their needs which means that they were self-sufficient.
As time passes, they left caves and lived in tribes and their demand for resources increased, because of new inventions such as clothing so they left animal skins, leaves and replaced with clothing. Now the time had come that human had to rely on others for resources, but here it was the question that how could they exchange resources with others, so the first adopted system was the barter system.
Under barter system goods are exchanged goods or services. Barter is a term for a system of exchanging things without the need for money. This system could only function in an extremely basic economy with low levels of production and consumption of products. Underdeveloped nations still employ this kind of bartering in their rural areas.
Barter system still in use in underdeveloped countries for example, when a country faces depression in economy, it exchanges the good which is abundant in production with other country for some other good such as wheat for rice, similarly it is still in use in rural areas where people take services from the barber or cobbler and in return, they pay wheat and other crops.
In today’s world, barter system is not used in main stream economies because now human desires have increased and diverse, economies are complex and there are number of difficulties in barter system which make impossible barter system to be used in today’s modern diverse economies.
Difficulties of Barter System
There are following difficulties of barter system given below:
1. Lack of Double Co-incidence of Wants
Double co-incidence of wants is an essential condition for barter. To understand this, we have to look at an example. Suppose a person wants to sell some wheat for rice. Now he must find another person who has rice and is willing to exchange rice for wheat. We can generate some conditions to understand better:
- There are two persons A and B.
- A wants to sell wheat and buy rice.
- B wants to sell rice and buy wheat.
It is so much difficult to find a person who wants to exchange goods under these terms so it is evident that this system has biggest flaw of double co-incidence.
2. Lack of Common Measure of Value
Lack of common measure of valuation or matric is an issue under barter system. Suppose two persons are ready to exchange goods. The problem of determining relative prices of their goods arises. It is difficult to ‘know what quantity of one good is given in exchange for the other. The party, which has more urgent and strong desire, will have to suffer by sacrificing a larger quantity of his commodity.
3. Indivisibility of Goods
Indivisibility of goods is another issue in barter system and create hurdle in barter exchange. For example, a person owns a horse and wants to get a pen. The value of horse, naturally, is much more than one pen. Thus the problem is how to divide the horse into small pieces.
4. Difficulty in Storing of Value
Another difficulty is lack of storing value. People want to save their valuable things for future, as we save money for future similarly suppose a farmer produces surplus wheat and he wants to store surplus wheat for his old age. But it is impossible for him to do so. Wheat will be wasted after a year or two. Similar is the case with many other commodities.
5. Difficulty in Borrowing and Lending
Borrowing and lending is another difficulty under barter system suppose a person lends wheat in draught or famine and take back that wheat in same quantity when the wheat is in abundance then he will be sufferer.
6. Difficulties in Government Taxes and Payments
In today’s world, taxes are collected in the form of money in easy form and paid to state employees as salaries but under barter system, it is so difficult that how taxes can be collected in the form of goods and how they can be paid to the state servants in the form of cows, wheat, shoes etc.
7. Difficulty in Transfer of Wealth
Transfer of wealth is another difficult issue under barter system. Suppose a person has valuable things such as cow, house, farm, goats in a country and he decided to move in another country so it will be so difficult for him to move all his wealth in the form of goods from one country to another.
Related Articles
Evolving different thoughts of Economics
2.1 Theory of Consumer Behaviour
2.2 Total Utility, Marginal Utility, Point of Satiety & Types of Utilities