Deflation and its Impact on Society. Deflation, the sustained decline in the general price level of goods and services, can have profound effects on an economy and society. This blog post explores the causes of deflation, its economic implications, and how it impacts businesses, consumers, and governments. Discover the challenges deflation poses to economic growth and stability, along with strategies used to counter its effects. Perfect for students and professionals alike, this post sheds light on a vital yet often overlooked economic phenomenon. This topic is equally important for the students of economics across all the major Boards and Universities such as FBISE, BISERWP, BISELHR, MU, DU, PU, NCERT, CBSE & others & across all the business & finance disciplines.
Table of Contents
Deflation and its Impact on Society
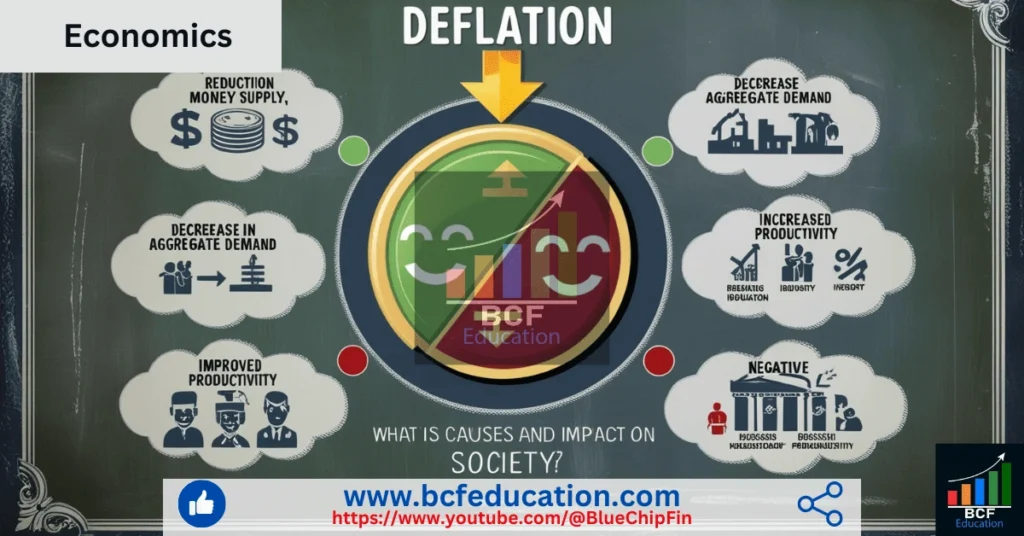
What is Deflation?
Deflation means sustained decrease in the general price level of goods and services over a period of time. In case of deflation, supply of goods and services are more than the demand of goods and services. Concept of Deflation is opposite to inflation.
The key causes of deflation include:
- Reduced Consumer Demand
Due to economic downturns, unemployment levels are high, incomes are low, people have no confidence in the economy, all these lead to reduced spending or demand. Under this situation, producers reduce prices to increase the demand.
- Technological Advancements
Technological advancements help to reduce production costs which ultimately leads to reduce prices of the products.
- Monetary Tightening
Reduced money supply and high rate of interest both leads to reduce spending. In result producers lower the prices to increase the spending behavior of the people.
- Excessive Supply
Another cause of deflation is excessive supply or over production, simply supply greater than demand leads to lower price level to increase the demand.

Impacts of Deflation on Society
Deflation can have both positive and negative impacts on society, depending on its extent and duration.
Negative Impacts
1. Economic Recession:
Due to persistent price fall, consumer spends less due to the fear of more fall in price in future, in result investment, revenues and demand declines which leads to economic recession.
2. Unemployment:
Due to less profits, businesses may cut employees to increase profits which leads to unemployment.
3. Debt Burden:
Deflation is damaging for borrowers because purchasing power increases or value of money increases but original debt remains the same on old agreed terms.
4. Bankruptcies:
Due to less investments, revenues, debt burdens and slow wheel of economy, companies and individuals may face insolvencies or bankruptcies.
5. Lower Wages:
To stay in the market, employers reduce the wages and salaries of the employees which may lead to generate negative sentiments among employees.
6. Reduced Investment:
Les revenues, less investments, slow moving economy discourages investors to invest in new projects which leads to slow growth of the economies.
Positive Impacts
1. Increased Purchasing Power:
Consumers get benefit from the deflation because of their increased purchasing power. They can increase their spending due to lower prices.
2. Encourages Savings:
Due to lower prices, consumption expenditures of consumers reduce so their portion of saving increases which is positive.
3. Efficiency in Production:
In deflation, businesses try to reduce their input costs to make more profits and these efforts leads efficient use of resources for the businesses through which they can obtain efficiency in production.
Conclusion
Deflation may be beneficial in the short run, but in the long run, it is damaging for the economy. Monetary and fiscal measures must be taken in the long run such as to reduce interest rates and to install new projects to stabilize the economy.

Related Articles
Money, Barter System and its Difficulties