1.What is Managerial Economics?, Theory of the Firm, Value of the Firm, Value Maximization – Dive into the fundamentals of managerial economics, a field that bridges economic theory with practical business decision-making. This blog post explores the definition and scope of managerial economics, its critical role in guiding managerial decisions, and how it relates to the theory and value of the firm. Designed for students and professionals alike, this article provides insights into how economic principles are applied in the real-world business context to drive strategic success. This topic is equally important for the students of Managerial Economics across all the major Universities such as MU, DU, PU & others & across all business & finance disciplines.
Table of Contents
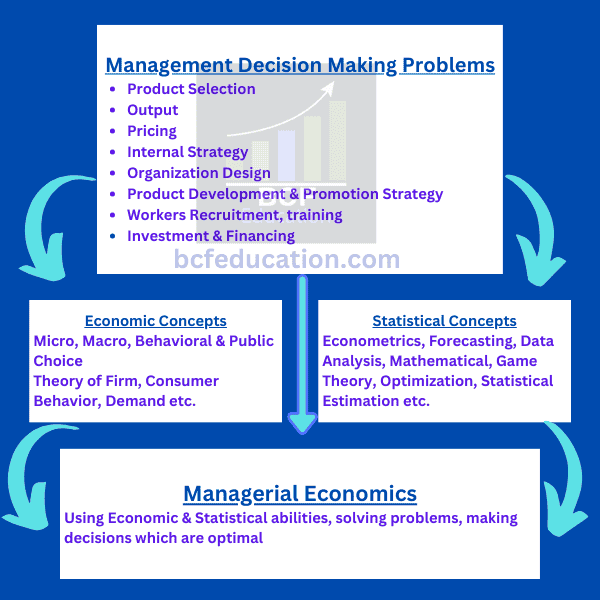
1.What is Managerial Economics?, Decision Making, Theory, and Value of Firm
How is Managerial Economics Useful?
- It helps managers, how economic forces affect organizations.
- It describes the economic consequences of managerial behavior.
- It describes that how to achieve goals of organizations efficiently.
- It bridges the link between economic concepts and different mathematical and statistical tools which are vital in decision making process.
- It helps and make possible the efficient and optimal use of resources to reduce cost and maximize profits.
- It is related to the short-run micro economic analysis.
Theory of the Firm
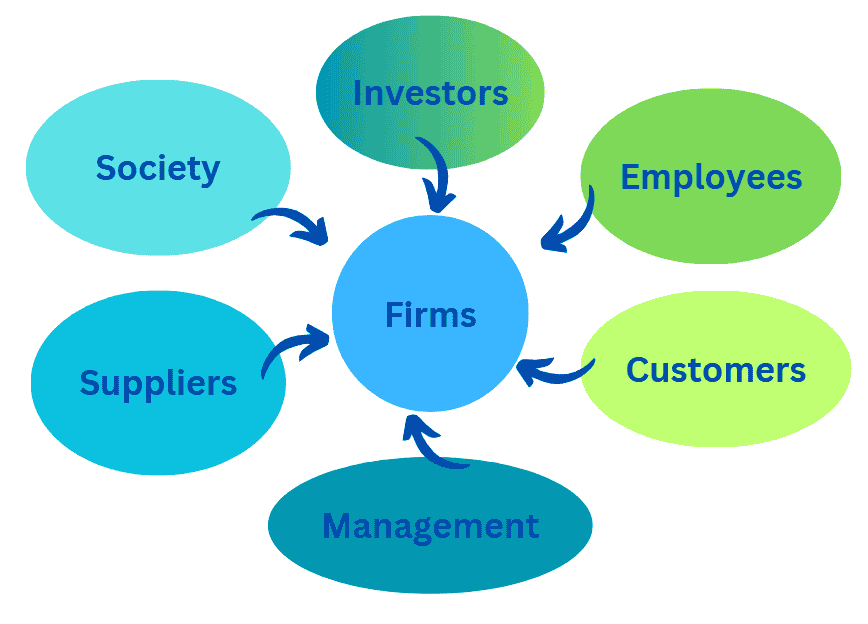
- Firms are useful for producing and distributing goods & services.
- In this process people are directly involved include customers, stockholders, management, employees, suppliers and society.
- Society is also involved because firms produces employment opportunities, pay taxes and provide goods & services to the society.
- Primary goal of the firm is to maximize profit & the firm’s managers will have to do maximize profits in the short-run & maximize expected value in the long-run.
- Value of the firm is the present value PV of the firm’s future cash flows.
Relation of Firms with Other Sectors
Value of the Firm
- It involves discount factor and as we know that it is the present value of firm’s future cash flows.
- Value of the Firm:
![]()
Where π = profit, n = time period and i=interest rate
As we know that profit π is = Revenue – Cost so We can say that:
![]()
Value Maximization Process
- In value maximization process all the departments play their respective roles e.g.
- Marketing and sales department focuses to maximize sales.
- Manufacturing & Production department will have to minimize costs.
- Administrative department will arrange the capital.
- Lot of other factors e.g. order size, quality, On-time delivery etc. simply all the forces emphasizes on to maximize revenue TR and to minimize costs TC to raise the profit.
- All these discussed above involve decision making process.
Constraints & The Theory of the Firm
Value Maximization Process
- In value maximization process all the departments play their respective roles e.g.
- Marketing and sales department focuses to maximize sales.
- Manufacturing & Production department will have to minimize costs.
- Administrative department will arrange the capital.
- Lot of other factors e.g. order size, quality, On-time delivery etc. simply all the forces emphasizes on to maximize revenue TR and to minimize costs TC to raise the profit.
- All these discussed above involve decision making process.
Constraints & The Theory of the Firm
- Managerial Decisions are made while taking constraints in the mind:
- Input Constraints:
- Outdated technology
- Scarce Resources
- Contractual Obligations
- Laws & Regulatory Restrictions
- Less skilled labor
- Limited availability of raw materials or inputs
- Output Constraints:
- Minimum Satisfaction Level
- Audience exposure for marketing exposure.
- Reliability requirement for electronic products etc.
- After sale services
Limitations of the Theory of the Firm
- Do Managers try to optimize (seek the best result) or satisfice (satisfactory result rather than optimal results)?
- It is impossible to give appropriate answer and this dilemma leads to other theories.
- There are some theories in which growth maximization is presumed to be a primary motive and managers concern with their own personal welfare and utility.
- Competition normally nudges the managers to grow the business.
- Stakeholders interests also push the managers to grow their businesses.
- Simply growth and value maximization is important for the breath of the business & equally important for stake holders, managers, owners & for business itself.
- It is considered that value maximization theory focuses on social responsibility too but traditional theory only focuses on profits and value maximization.
Business/Accounting Vs. Economic Profit
- Business/Accounting Profit
- As we know that profit is equals to:
- Profit = Revenue – Costs
- In Accounting profit, we deduct only explicit costs from the revenue so we can say that:
- Business/Accounting Profit = Revenues – Explicit Costs (Cash Costs) those purely injected as input to produce output.
- Whereas Economic profit = Revenue – (Explicit Costs + Implicit Costs)
- Implicit costs are non-cash costs such as opportunity cost.
- Opportunity cost is simply the loss of other alternative when one alternative is chosen.
- It is important to note that when business earns normal profit, The NPV Net Present value of economic profit will be zero.
- Every business needs at-least Risk-Adjusted Normal Rate of Return on his invested capital where Risk-Adjusted Normal Rate of Return is the minimum return needed to retain and attract the investment, where risk premium involves which is important component of CAPM model in which Risk Premium is equals to:
- Risk Premium = Market Risk – Risk Free Rate of Return
- We are considering risk here because return has strong positive relation with risk.
Variability of business Profits
- Profit fluctuates widely
- Average business Profits measured in dollar terms or as a percentage of sales revenue is called profit margin.
- Whereas economic concept of profit is measured in terms of realized rate of return on stock holder’s equity where ROE is equals to:
![]()
Why do Profits Vary Among Firms?
Disequilibrium Profit Theories
Many Firms earn significant economic profits whereas some experience significant losses. Why?
Frictional Profit Theory
States that disequilibrium due to unanticipated or unexpected changes in demand or cost may cause unanticipated shocks which finally results positive or negative economic profits for some firms.
Monopoly Profit Theory
Is an extension of Frictional Profit Theory in which we know monopolist firm earns huge above normal profits because of its nature that the firm is only producer and price setter, no competitors and economies of scale.
Compensatory Profit Theories
This theory was presented by Joseph Schumpeter.
This theory of profits explains that economic profits arise because of successful innovations introduced by the entrepreneurs.
According to Schumpeter any new measure or policy adopted by an entrepreneur to reduce his cost of production or to increase the demand for his product is an innovation.
Thus innovations can be divided into two categories:
First types of innovations are those which reduce cost of production e.g. new machinery, new and cheaper technique or process of production, exploitation of a new source of raw materials, a new and better method of organizing the firm, etc.
Second types of innovations are those which increase the demand for the product. In this category are included the introduction of a new product, a new variety or design of the product, a new and superior method of advertisement, discovery of new markets etc.
Compensatory or Managerial Efficiency Theory of Profits
Lastly, this theory recognizes that some firms are more efficient than others in terms of management of productive operations and successfully meeting the needs of consumers.
Firms with average level of efficiency earns average rate of return. Firms with higher managerial skills and production efficiency are required to be compensated by above-normal profits (i.e. economic profits).
Therefore, this theory is also called compensatory theory of profits.
Role of Business in a Society
- Firms will have to earn above normal profits with projects having positive NPVs.
- Boeing earns above normal profit using compensatory theory of profit.
- Microsoft earns above normal profits using all four theories of profits and has monopoly of profits due to their copyrights, and specifically through innovations.
- Google, IBM, Oracle are hosts of others.
- Above normal profits signals that output has increased.
- Above normal profits overall benefit the society, make more innovation and productivity possible, create greater incentives and it boosts the economic expansion and growth of firm and society too by creating more employment.
- Below normal profits create stagnation and inefficiency.



